Navigating the Future: How Mosaic’s High-Resolution Cameras are Reshaping Data Collection in Utilities and Telecom for FTTH/FTTX planning
Introduction
In the interconnected fabric of today’s utility and telecommunication landscapes, the ability to capture comprehensive street view imagery is not a luxury—it’s a necessity. The once manual task of surveying vast networks of infrastructure has been revolutionized by the advent of 360° mobile mapping cameras. This technology is now pivotal in constructing a digital canvas upon which the future of these industries will be designed and managed.

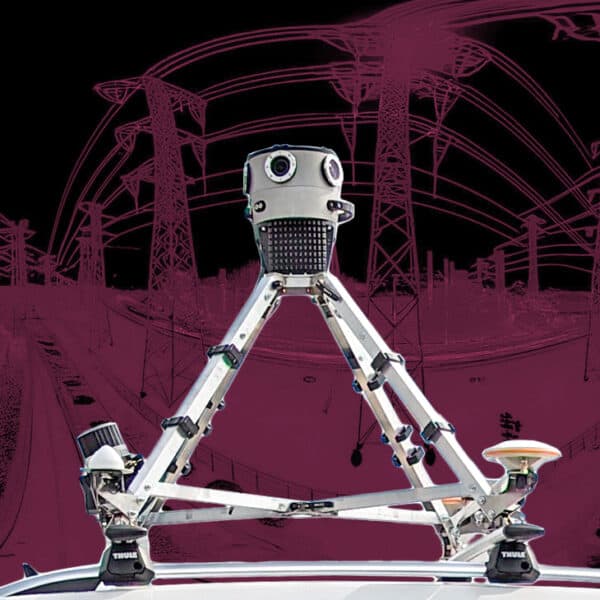
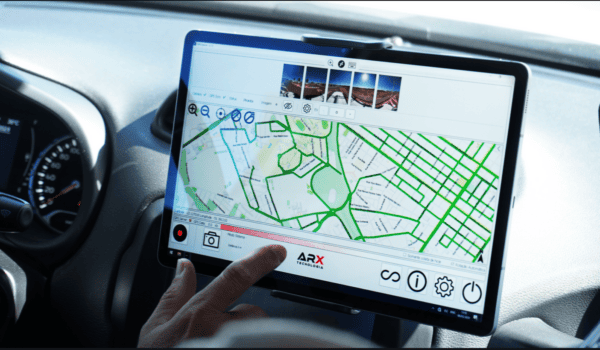
The integration of Mosaic cameras represents a significant technological leap forward. The industry-leading line of Mosaic cameras, ranging from 12K to 20K imaging, equips companies with the most robust and highest-resolution tools on the market. These cameras are not just devices but comprehensive solutions, providing an all-in-one system with on-board GPU that requires no additional computer for operation.
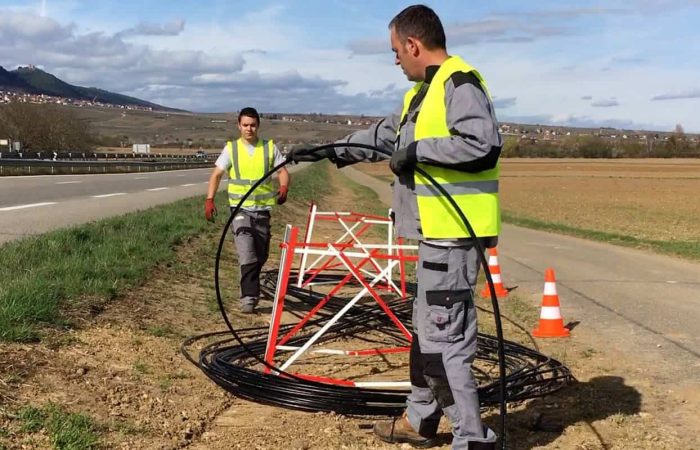
For industries like utility and telecom, which are now grappling with the colossal task of rolling out FTTH/FTTX infrastructure, the Mosaic camera systems are a game-changer. They offer the clarity, resolution, and durability to capture detailed street view imagery, essential for planning and maintaining expansive networks.

This enhanced capability to collect and analyze data at scale allows even those companies new to surveying or mobile mapping to gain deeper insights than ever before, streamlining their operations and making informed decisions to propel their services into the future.
The Evolution of Data Collection in Utilities and Telecommunications
The journey from rudimentary manual surveys to the sophisticated capture of geospatial data is a story of relentless innovation. Initially, utilities and telecom companies relied on physical surveys and satellite imagery to gather necessary data—a process fraught with time delays and imprecision. These methods often resulted in a mosaic of data that lacked the resolution and frequency needed for fine-tuned decision-making. As technology advanced, the industry’s tools became more adept at capturing the nuances of the physical world, setting the stage for a new era of data collection.
Over the last century, data collection within utilities and telecommunications has undergone significant changes, evolving through various stages of technological advancement. Let’s delve into the transformation and its implications.
The Past: The Analog Age and Early Digital Transition
In the early stages, data collection was largely manual, characterized by:
- In-person site assessments and physical surveys.
- Paper-based records and archiving, leading to difficulties in data access and inconsistencies.
- Long processes for obtaining governmental data, such as mailing FOIA requests and waiting for responses.
The Shift: Digitalization and Geospatial Mapping
As digital technology began to permeate the industry, a notable shift occurred:
- Transition to online records, drastically improving the efficiency of data retrieval.
- Introduction of geocoding, connecting address data with geographic coordinates, which allowed for better integration of data into mapping technologies.
- Digital photography, which enabled immediate use and incorporation of images into reports and assessments.
The Present: Standardization and Advanced Data Tools
The industry has moved towards:
- Standardized processes for environmental risk management, leveraging technology for efficiency.
- Utilization of more advanced technology tools, including GIS, for in-depth data analysis and visualization.
Check out this great article showing 12 Methods for Visualizing Geospatial Data on a Map
The Future: Integration of AI and Collaborative Technologies
Looking forward, the industry is expected to see:
- Collaborative virtual site visits using real-time satellite imagery.
- AI and augmented reality to enhance data collection and analysis.
- Unified systems that can integrate various data types, with the potential for automated data population from live feeds.
In summary, data collection in utilities and telecommunications has transitioned from manual, time-consuming processes to efficient, technology-driven methods. This evolution has enabled quicker access to more accurate and comprehensive data, facilitating better decision-making and strategic planning within the industries.
Rising Trends in Geospatial Data Capture
The landscape of geospatial data capture is currently experiencing a paradigm shift. Companies are moving towards in-house data acquisition, driven by a need for real-time data and autonomy over their operations. This trend is facilitated by the advent of technologies that allow for rapid processing and visualization of geospatial information. Real-time data capture has become crucial for timely decision-making and is now seen as a competitive edge in an industry where the stakes for efficiency and reliability continue to rise.
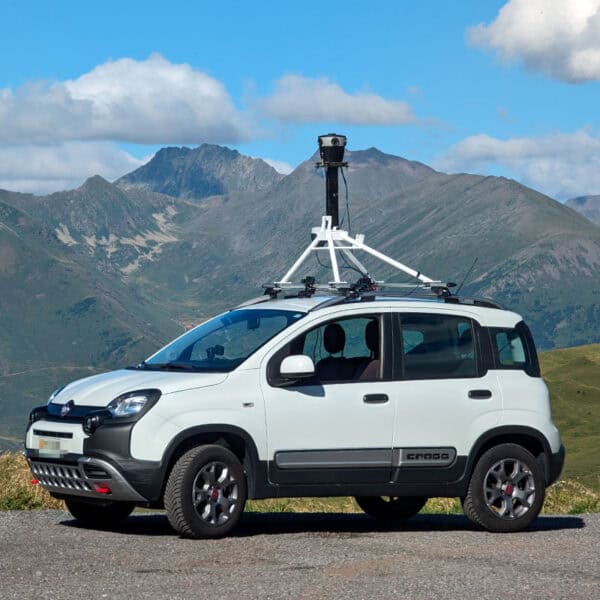
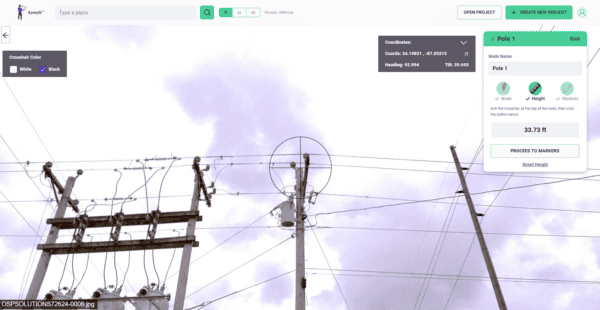
The advent of the Mosaic camera systems which changed the game in recent years by introducing the highest resolution, single standalone units on the market, all in a user-friendly and robust unit. The systems offer unprecedented clarity, allowing utility companies to capture the truest image possible of their existing infrastructure and potential FTTH/FTTX deployment routes.
360° Mobile Mapping Cameras: A Technological Leap

The introduction of 360° mobile mapping cameras has been nothing short of a technological leap for data collection. These sophisticated devices, mounted on various vehicles, capture panoramic images and detailed environmental data far beyond what was previously possible. Their robust sensors and advanced imaging capabilities eclipse the limited scope and resolution of traditional survey methods, offering a dynamic and comprehensive view of physical spaces that is revolutionizing the industry.
Mosaic Camera Systems: An Industry Game-Changer
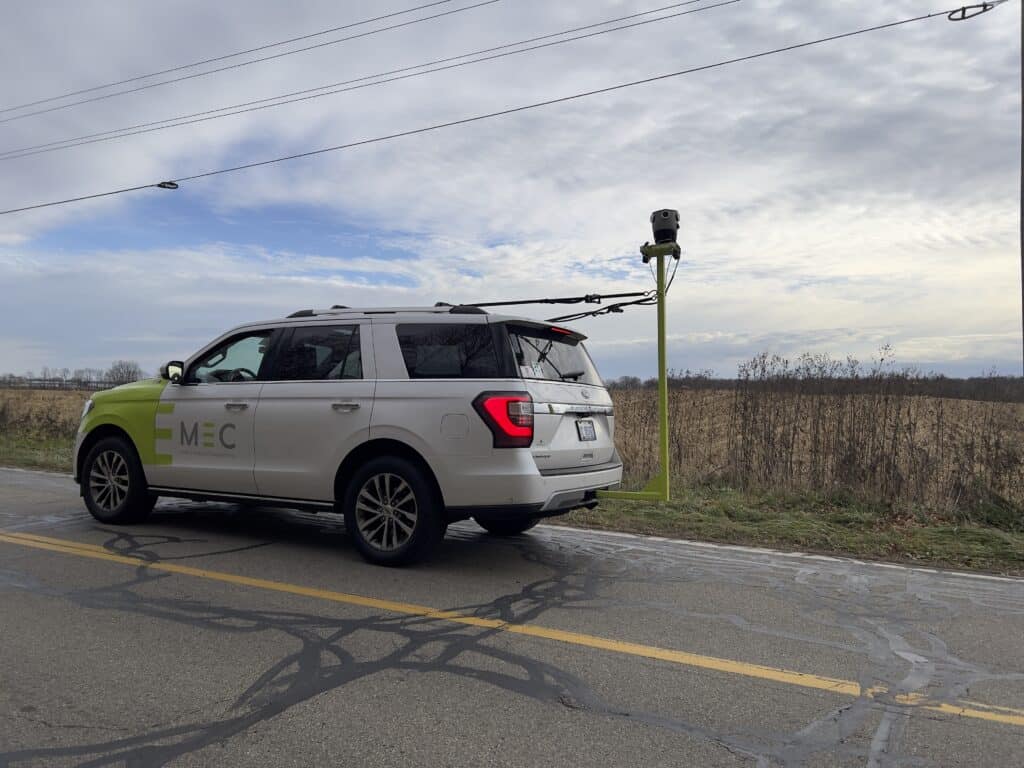
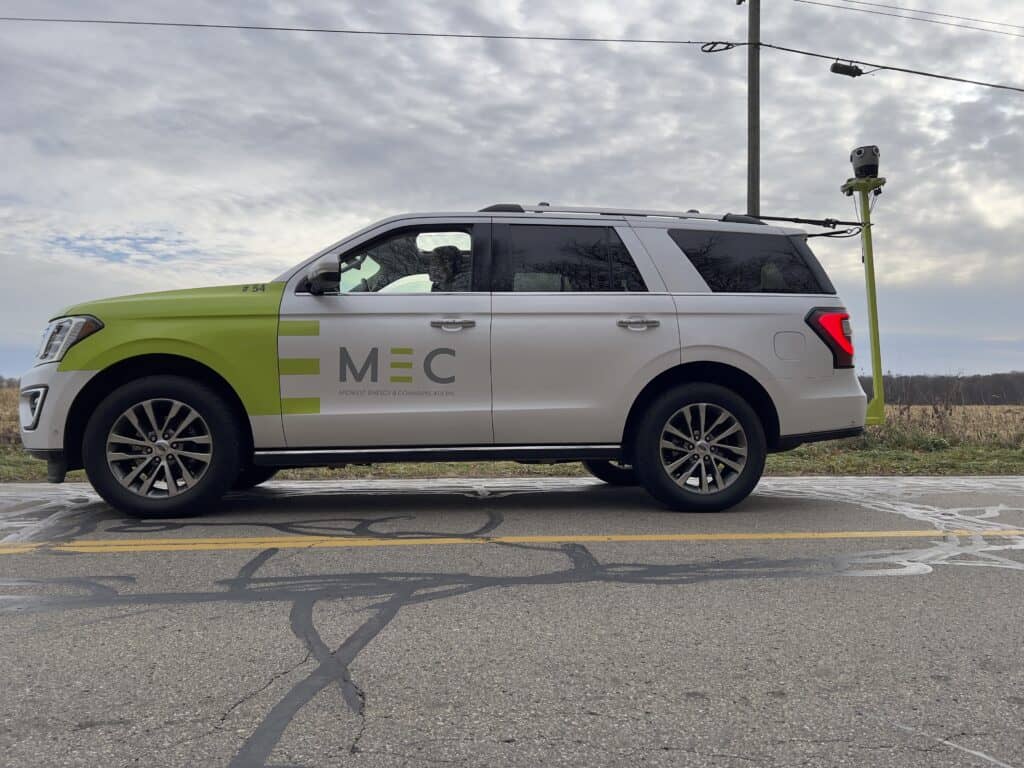
Among the vanguard of this revolution is the Mosaic 51 and Mosaic X cameras. Both have been deployed by various utility and telecommunication providers and service providers around the world.
Among them are Catsurveys located in the United Kingdom and Midwest Energy & Communications in the central United States.
You can read their case studies here to learn about the innovation they are bringing to their data capture methods and the benefits that they and their end users are experiencing.
Midwest Energy & Communications Case Study →
The camera’s high-resolution imaging at speeds up to 55 mph, impeccable stitching to create seamless panoramic views, and machine learning-ready data sets presented a quantum leap in quality and efficiency for the company. The operational benefits were immediate: enhanced safety, better planning, and a significant reduction in the need for repetitive site visits.
Specific Use Cases for 360° Street View Imagery
The utility of 360° street view imagery is vast and varied:
Asset Management: Detailed imagery facilitates the meticulous inspection and management of infrastructure assets.
Route Planning: Utilities benefit from precise mapping to navigate complex networks and plan new expansions.
Environmental Impact: Accurate imagery helps in assessing the environmental impact of existing and planned infrastructure.
FTTH/FTTX Rollout: With the boom in funding for fiber networks, specifically in the United States, 360° imagery is indispensable in the planning and implementation of FTTH/FTTX, ensuring that every fiber optic cable is laid with precision.
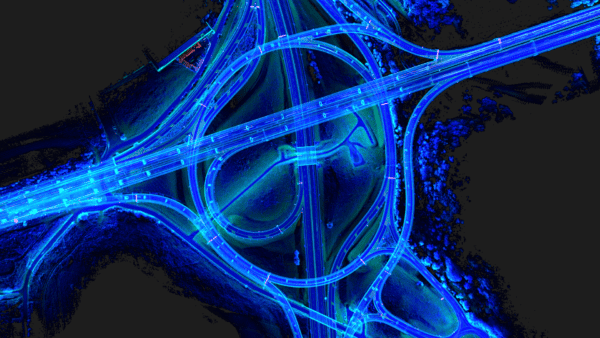
In the context of FTTH/FTTX, the Mosaic camera operators have the option of integrating with laser scanners, enabling high-speed photogrammetry and 3D modeling, essential for detailed planning and efficient maintenance of fiber networks.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) with 360° mobile mapping systems is redefining the scope of data analytics. These technologies convert vast datasets into predictive tools and actionable insights. ML algorithms excel in recognizing patterns and anomalies in infrastructure, facilitating preemptive maintenance actions and enhancing the longevity and reliability of utility networks.
This is especially true when dealing with the fine-grained details necessary for FTTH/FTTX infrastructure. To reliably train models for tasks such as detecting fissures in conduits, identifying encroaching vegetation on overhead cables, or assessing wear and tear on utility poles, the highest resolution imagery is vital. Cameras like the Mosaic 51 and Mosaic X, which capture 12.3K and 13.5K respectively resolution images, provide the level of detail required for these AI-driven tasks.
Small details, like the subtle bend in a fiber line that may indicate stress or the early signs of insulation wear on cables, can be the difference between preventative maintenance and a costly reactive repair. AI models trained on high-resolution imagery can discern these nuances, leading to more accurate and predictive analytics. This capability ensures that utility companies can maintain the integrity of their infrastructure with greater efficiency and foresight.
Challenges and Considerations
While the advent of mobile mapping technology heralds a new era of data collection and infrastructure management, adopting it at scale introduces complex challenges.
Beyond technical complexities and the need for skilled operators, economic factors play a critical role. For surveying to be viable on a large scale, companies require an economical solution that spans from data capture to processing.
Ownership of the data is another crucial aspect; companies need assurance that they can securely store and manage their proprietary information without dependency on third-party platforms. This independence is essential not only for operational integrity but also for maintaining a competitive edge in the fast-evolving landscape of utility and telecommunications.
Data privacy and cybersecurity are also paramount, necessitating robust strategies to protect sensitive information from breaches, which becomes increasingly complex as the volume and detail of collected data grow.
The Future of Funding in FTTH/FTTX Planning
As the U.S. ramps up funding for FTTH initiatives, the role of advanced mapping technologies in optimizing these investments becomes increasingly significant. Such funding is expected to enhance the national broadband infrastructure, and mobile mapping cameras will be critical in ensuring these projects are designed and executed efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing coverage.
What is FTTH/FTTX and why is it important?
FTTH (Fiber to the Home) and FTTX (Fiber to the Premises) are technologies that involve the installation of optical fiber from a central point directly to individual buildings such as residences, apartment buildings, and businesses to provide high-speed internet access. These technologies have significant implications for connectivity and are becoming increasingly important in the U.S. for several reasons:
Quality of Service: FTTH offers unparalleled data speeds and reliability, surpassing traditional broadband delivery methods. It ensures low latency and high uptime, essential for modern internet usage which includes streaming, online gaming, and telecommuting.
Economic Impact: High-quality broadband is linked to increased productivity, better access to healthcare and education, and enables rural living by providing the infrastructure needed for remote work and entrepreneurship.
Government Funding: The recent surge in FTTH deployments in the U.S. has been propelled by significant government funding initiatives such as the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program, the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF), and ReConnect. These programs aim to bridge the digital divide and provide high-speed internet access to underserved areas.
Digital Equity: The expansion of FTTH is seen as a step towards digital equity, ensuring that all members of society have access to high-speed internet. This is crucial for full participation in the economy and society, from accessing government services to educational resources.
The focus on FTTH and FTTX is part of a larger effort to upgrade the U.S. telecommunications infrastructure, making it future-proof and capable of handling the increasing demands of consumers and businesses alike. The funding for these initiatives often comes from federal and state programs aimed at improving national broadband coverage.

Broader Implications for the Industries
The implications of mobile mapping technologies are far-reaching for the utility and telecommunications industries. They streamline operations, yielding substantial cost savings and enhancing service delivery. Accurate data aids in strategic planning, providing a competitive edge and fostering improved customer satisfaction by ensuring more reliable service.
Future Outlook and Scalability in FTTX Planning
The potential for the technology to evolve is boundless. As the industry standards shift towards more sophisticated data collection and analysis methods, companies must stay agile, ready to adapt to and adopt future advancements that promise even greater efficiencies and capabilities.
Looking into the future, the Mosaic Viking camera, boasting the highest resolution among mobile mapping cameras on the market, delivers the required imagery data for the rapidly expanding FTTH/FTTX networks, ensuring that companies can keep pace with the growing demand for high-speed internet connectivity
Conclusion
The transformative impact of 360° mobile mapping cameras is undeniable. As the utility and telecommunications sectors continue to harness this powerful technology, they pave the way for a future where infrastructure planning and management are conducted with unparalleled precision and insight.
Are you looking for a faster, easier, and more robust way to collect street view data in your FTTX/FTTH rollout?
Contact us at Mosaic so we can help find the right solution for you.