Throughout 2023, we have had the opportunity to speak with our (prospective) customers, partners, and even competitors, and it has given us highly valuable insights into what the industry needs and where trends are going. Looking at the geospatial industry as a whole, we predict a surge in the demand for clearer, more detailed imagery. This demand drives the development of innovative tools that enable efficient mapping in various environments, from bustling city streets to remote landscapes.
The integration of diverse technologies, especially artificial intelligence, is expected to streamline the mapping process significantly. AI’s ability to swiftly process vast amounts of data is not just a boon for efficiency but also enhances the accuracy and usability of the mapping outputs.
Mobile scanning technologies are emerging as key players, particularly in urban settings where traditional mapping approaches struggle. These technologies are becoming more agile and cost-effective, allowing for rapid data collection that is both accurate and scalable. This evolution is crucial for sectors such as Digital Twins, Smart Cities, and AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction), where up-to-date and detailed environmental data are invaluable.
Furthermore, the industry is moving towards more user-friendly platforms, enabling a broader range of applications and users to engage with mobile mapping technologies. From entertainment industries like TV/film production and video games to more technical fields such as surveying, BIM, and infrastructure inspection, the accessibility of high-quality mapping data is transforming workflows and creative processes.
In 2024, advancements in technology will characterize the mobile mapping industry, making high-quality, detailed mapping more accessible and affordable. The integration of AI, improvements in mobile scanning technologies, and a focus on user-friendly platforms are shaping an era where detailed and accurate geospatial data becomes a cornerstone for a myriad of industries and applications. As these trends unfold, they promise to unlock new levels of efficiency, creativity, and understanding of the world around us.
Below is our deep dive into the biggest trends we see for the coming year and beyond.
The Rising Importance of Imagery in Geospatial Mapping
Having firmly established ourselves among the leaders in geospatial imagery, particularly in the mapping industry, we’ve been at the forefront of exchanging ideas and experiences with partners and customers. This has allowed us to witness a significant shift in the geospatial and mapping industry. The focus is increasingly on achieving precision through calibrated photographic imagery rather than solely relying on LiDAR data. This change aligns with a broader trend where end users, often without extensive technical expertise, find images more useful and easier to comprehend.
While high-precision GNSS, IMU devices, or LiDAR point clouds remain essential for tasks like 3D modeling and precise measurements, the fundamental value is now seen in the imagery itself. This trend underscores the significance of visual data in delivering comprehensive and easily understandable information. Many customers have realized that their need for high spatial accuracy, once paramount, can often be met sufficiently through detailed images. These images, enriched with data from high-precision devices, offer a balanced blend of clarity and detail necessary for various applications, ranging from urban planning to environmental monitoring.

Compact and Versatile Data Capture Devices
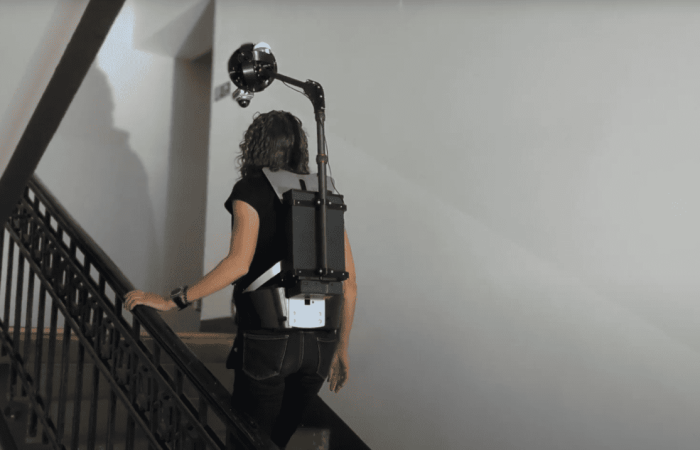
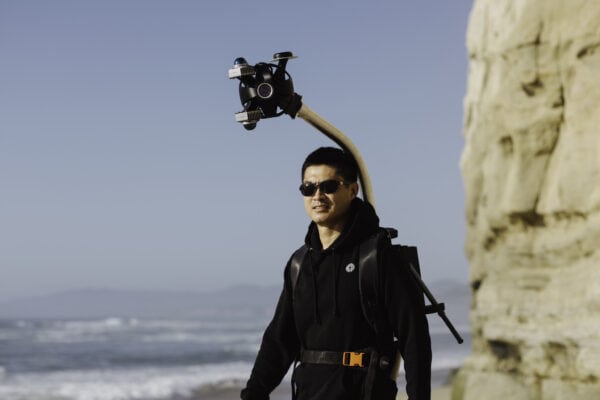
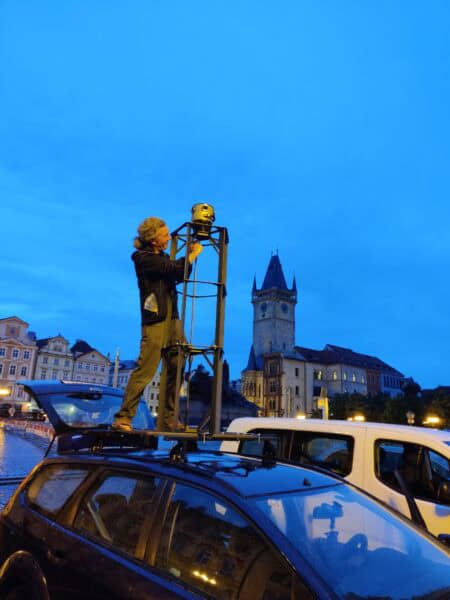
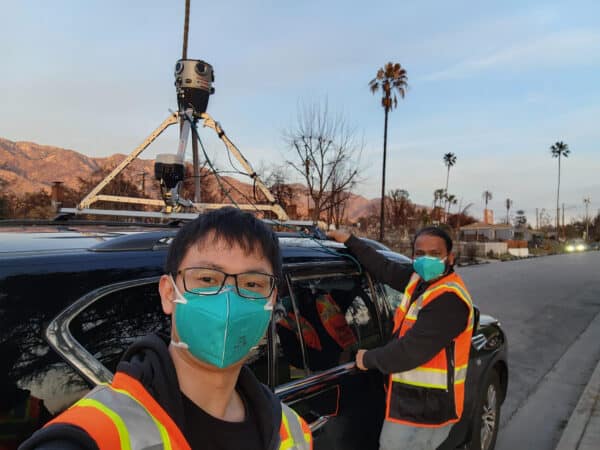
One significant trend we notice is the shift towards more compact and versatile data capture devices. This shift is a response to the limitations of traditional vehicle-based Mobile Mapping Systems (MMS) in dense urban areas. The industry is evolving with innovative solutions like backpack-mounted systems, handheld devices, and drones tailored for navigation and data capture in narrow streets and heavy traffic.
These smaller, agile devices enable mapping at walking or biking speeds, proving invaluable in tight urban spaces. Backpack systems equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors facilitate detailed data collection in crowded areas, while handheld devices offer quick and efficient capture capabilities, ideal for indoor environments or small-scale projects.
Drones, or Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), are increasingly employed for their aerial perspective, especially in inaccessible or challenging ground areas. These compact devices not only excel in maneuverability but also in data quality and processing speed, with advanced sensors, LiDAR, and GNSS technology ensuring accuracy and detail.
The incorporation of wearable technology in mobile mapping, embedding devices in clothing or accessories, further highlights the industry’s move towards seamless, natural data collection in dynamic environments. This evolution marks a significant step in urban mapping, offering more efficient, detailed, and accessible geospatial data collection, a game-changer for various sectors relying on up-to-date and comprehensive mapping information.
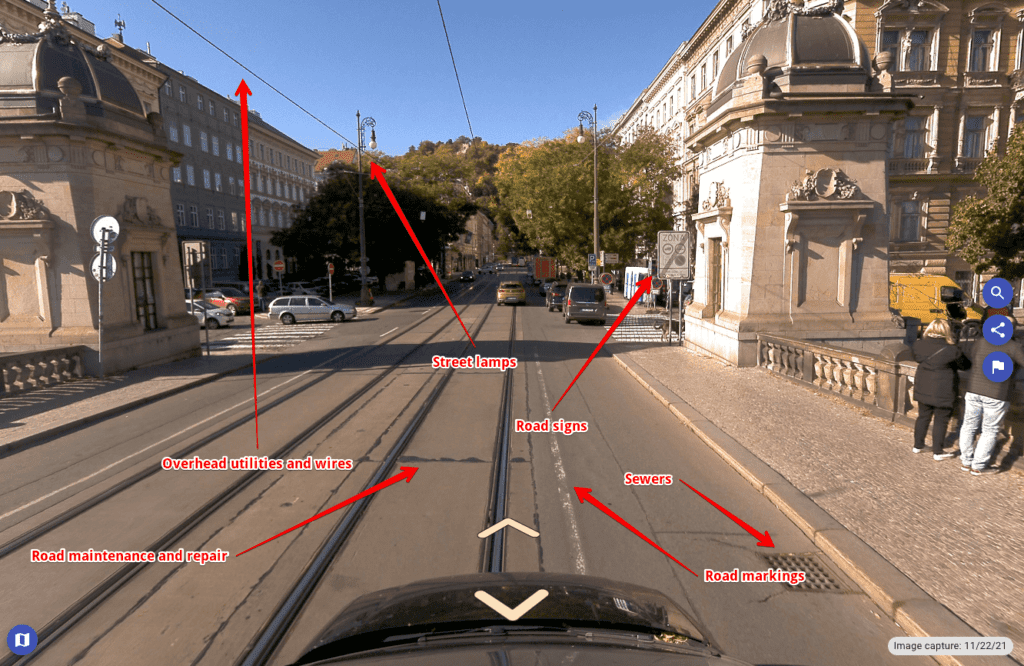
Emphasis on Multimodal Geospatial Solutions
The emphasis on multimodal geospatial solutions is increasingly critical, reflecting a trend toward integrating various technologies for comprehensive data capture. These solutions synergize the capabilities of high-resolution cameras, LiDAR, GNSS, and a wide array of sensors into a cohesive and adaptable framework. This multidisciplinary approach caters to the need for versatile data collection across different terrains and under varying lighting conditions.
For instance, in urban environments, the combination of LiDAR and photographic imagery enables detailed 3D mapping of buildings and infrastructure, while GNSS technology ensures precise location tracking.
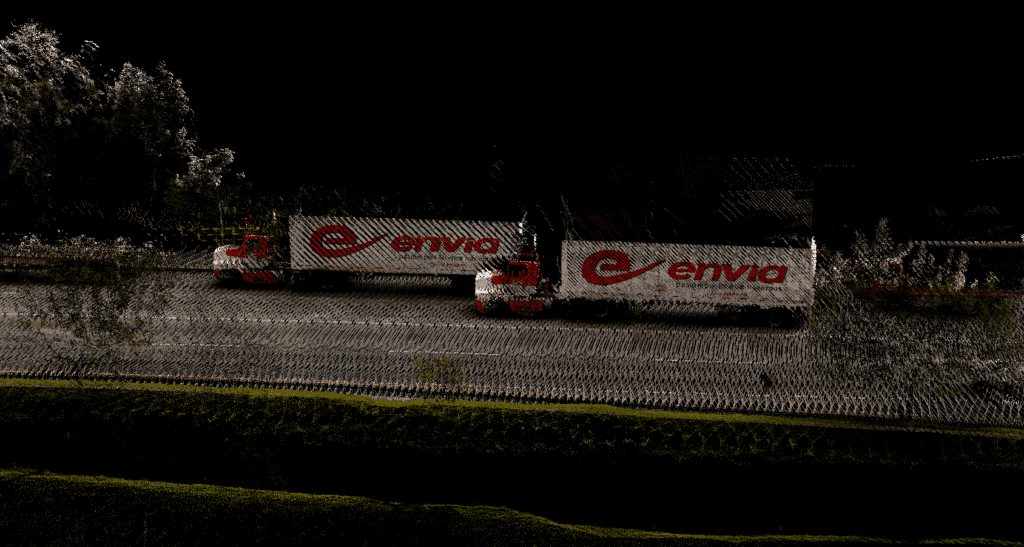

In natural landscapes, these systems adapt to capture topographical variations and environmental changes, with sensors that can detect everything from vegetation health to water quality.
Integrating thermal imaging and night vision technologies extends mapping capabilities into different times of the day, which is crucial for applications like wildlife monitoring and security.
Indoor mapping, too, benefits from this multimodal approach, with systems that combine laser scanning and photogrammetry to create detailed interior layouts. Additionally, emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) are being integrated, allowing for real-time data overlay and enhanced user interaction with the mapped environments. This trend towards multimodal systems signifies a leap in the efficiency and scope of geospatial applications, enabling a more detailed, dynamic, and practical understanding of both man-made and natural environments.
Advancements in Data Processing and AI Integration
Advancements in data processing and AI integration represent a pivotal area of growth and innovation in mobile mapping. The roles of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have become increasingly crucial, transforming the landscape of geospatial technology. These cutting-edge technologies enable more efficient and informed decision-making processes by rapidly analyzing vast quantities of collected data.
AI-driven analytics are adept at identifying patterns, predicting changes, and providing deep insights that were previously unattainable, especially in real-time mapping scenarios. For example, AI can be used for detecting and managing infrastructure vulnerabilities, like identifying hazardous utility assets that could potentially lead to fires. It also plays a vital role in environmental conservation, for instance, by monitoring deforestation rates to facilitate more effective ecosystem management. Utilizing a blend of advanced technologies, AI contributes significantly to the greening of cities. In the realm of urban planning, it is instrumental in optimizing traffic flow and enhancing overall urban design through the analysis of pedestrian and vehicular traffic patterns.
This revolution in data processing has opened doors to more dynamic mapping capabilities, enhancing accuracy and predictive power in various applications. It allows for automating complex data interpretation tasks, reducing the time and human resources needed for analysis. Furthermore, integrating AI and ML in mobile mapping tools leads to continuous improvement of the systems as they learn from new data, constantly refining their algorithms for better performance. This evolution heralds a new era in which geospatial data becomes a more powerful tool for understanding and interacting with our physical world, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation in areas ranging from urban planning to environmental monitoring.

Safely Scanning Inventory on the Move
The demand for scanning inventory on the move has catalyzed the creation of advanced mobile mapping solutions, addressing the unique challenges of densely populated urban landscapes. Traditional mapping methods often struggle in these environments, but the new generation of mobile mapping technologies excels by providing high-quality data capture at pedestrian speeds. This development is a significant breakthrough, especially for areas with limited or impractical vehicle access.
For instance, in historic city centers with narrow streets or pedestrian-only zones, these mobile solutions can efficiently navigate and collect detailed spatial data, something previously challenging with conventional methods. The advent of ‘hands-free’ scanning technologies enhances safety significantly. These systems minimize the risk of accidents or mishaps, especially in busy or confined spaces, by allowing operators to stay fully aware of their surroundings without the burden of handheld devices. This method not only improves the safety of the personnel involved but also ensures the integrity of the data collected by reducing the likelihood of errors or interruptions during the scanning process.
Redefining Documentation and Preservation
The utilization of 360° imagery is rapidly transforming various sectors. This innovative technology is not only revolutionizing the tender documentation process by encouraging more competitive bids and reducing final tender prices but also enhancing decision-making with comprehensive visual information. Moreover, it serves as a valuable tool for documenting site changes and has broader applications in facilities management, education, and infrastructure projects. Unlike traditional surveying methods, 360° imagery provides detailed visual information, making it particularly useful for heritage sites and preservation efforts. With its advanced imaging technology, characterized by high-resolution visuals, 360° imagery offers an unparalleled user experience and utility, further expanding its horizons.
In conclusion, the trends and innovations in mobile mapping for 2024 are reshaping the industry by focusing on user-friendly, adaptable, and image-centric technologies. These advancements align with the practical needs and preferences of users, guiding us toward a future where geospatial technology is not only more accessible but also more efficient and versatile. The integration of AI and machine learning is set to revolutionize various sectors, including urban development and environmental preservation. It offers unprecedented opportunities for innovation and enhances our understanding of the world.