Leveraging Advanced Mobile Mapping Solutions for Reality Capture with Mosaic Cameras
While reality capture has been there for decades, modern development and increasing interoperability of different technologies have made it a game-changer in the geospatial industry.
Modern reality capture is bringing a lot to the table: 3D digital models that you can spin, measure, and analyze right on your screen. These models range from single objects and buildings to vast areas and environments, with unprecedented levels of accuracy, detail, and efficiency.
Let’s look closer at what has been moving the quality of 3D digital snapshots of the real world forward and how it transforms collaboration and workflows within GIS, the mapping industry, and BIM.
Understanding reality capture for every level of detail, regardless of scale
Modern reality capture uses high–definition images and/or laser scanning devices to create a digital replica of objects, assets, buildings, or natural environments. The technology involved reflects the size, location, and aspect that is supposed to be captured.
Depending on the level of detail required, the outcome can be a real-life and geo-referenced digital twin of anything from a building or a construction area to entire cities or kilometers of roads and their environments.
This naturally transforms operations for all companies and organizations involved in the geospatial industry, regardless of the scale or stage of the project. Capturing existing conditions, planning, quality assurance, and conceptual changes can be implemented much faster, easier, more accurately, and with fewer human resources.
The motion of modern reality capture
The process of creating a 3D model starts with choosing the right technology:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) scanner measures distances by illuminating a target with a laser beam and analyzing the reflected light to create precise point clouds of objects and environments. One of the main benefits of 3D scanning LiDAR technology is its ability to capture large amounts of data quickly. This is especially useful for mapping and surveying large areas such as cities, industrial sites, and natural landscapes.
Photogrammetry uses high–definition photographs from at least two vantage points to create 3D computer models. Typical products are orthophotos, digital elevation models (DEMs), 3D point clouds, and textured 3D models.
High-resolution 360-degree cameras like Mosaic´s mobile mapping camera systems capture complete spherical views of their surroundings in a single shot through multiple synchronized sensors. In geospatial applications, these cameras:
- Create immersive panoramic imagery for virtual site visits
- Document existing conditions of infrastructure
- Support reality capture for digital twin creation
- Enable rapid field data collection
- Integrate with more robust mobile mapping systems
These technologies don’t operate in isolation; they seamlessly integrate with Geographic Information Systems (GIS), mapping platforms, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) software. This enables professionals across industries – from architecture and construction to urban planning and heritage preservation – to create incredibly accurate digital representations of real-world spaces.
GIS platforms for tabular data from reality capture
To fully exploit, store, and analyze the 3D digital models produced by reality capture technologies, the acquired data must be attached to a unique location or, more precisely, geo-referenced. This is where GIS becomes an essential part of reality capture (and vice versa).
The importance of GIS data integration lies in its ability to pull together the vast amounts of information necessary to balance competing priorities in various areas. This includes
- urban planning – e.g., optimizing new building placement or determining the feasibility of a waste disposal site,
- environmental management – such as natural resource management, land use planning and conservation, or pollution control and monitoring, and
- infrastructure development includes energy transition and distribution, construction and transportation management, and environmental assessments.
The role of GIS in reality capture
GIS fundamentals
Integrating reality capture data with GIS platforms enables a range of analytical capabilities. GIS can process precise and detailed digital data into contours, orthomosaics, 3D rasters (including digital terrain and surface models), hillshades, and 3D scenes.
This integration bridges 2D to 3D analysis of terrain and surface features. The combination of GIS and modern reality capture data accuracy provides valuable datasets for analyzing the earth’s surface and landscape.
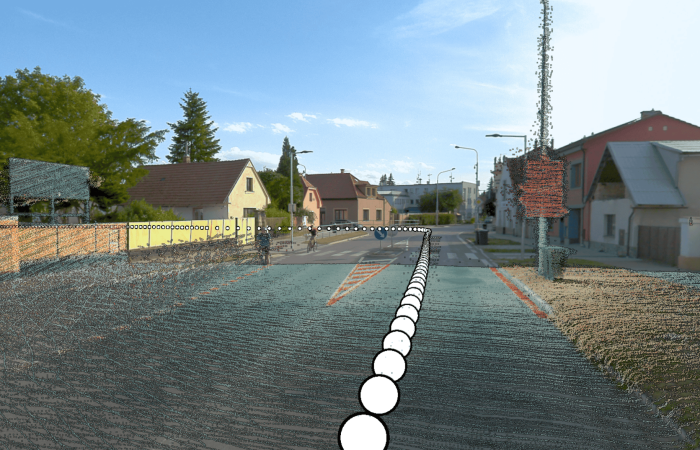
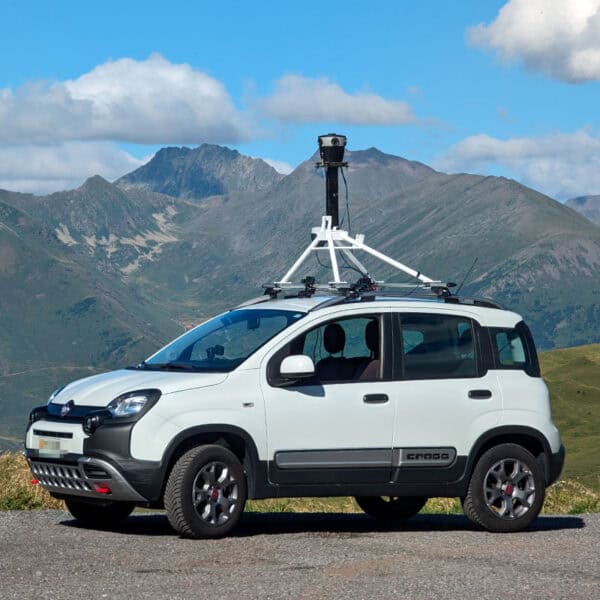
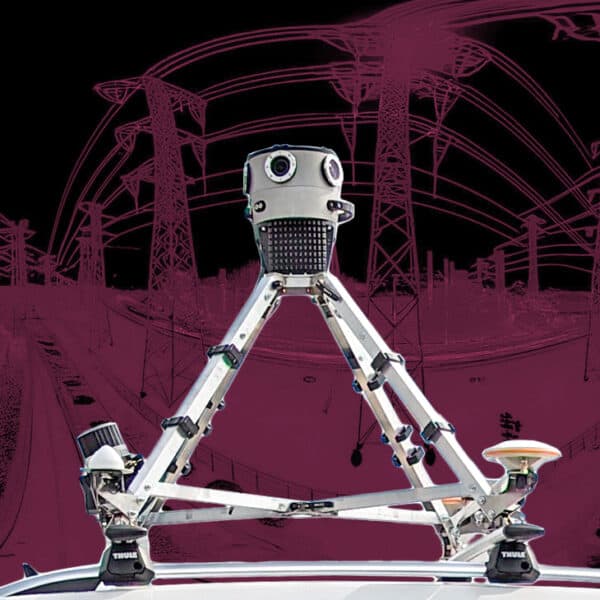
Precision and detail are among Mosaic mobile mapping cameras’ most prominent driving forces. Equipped with onboard GNSS receivers and being able to reach up to 12.3K resolution captures, our 360-degree imagery solutions (Mosaic 51) are ready to deliver geo-referenced and extremely detailed 3D models of large–scale environments and assets.
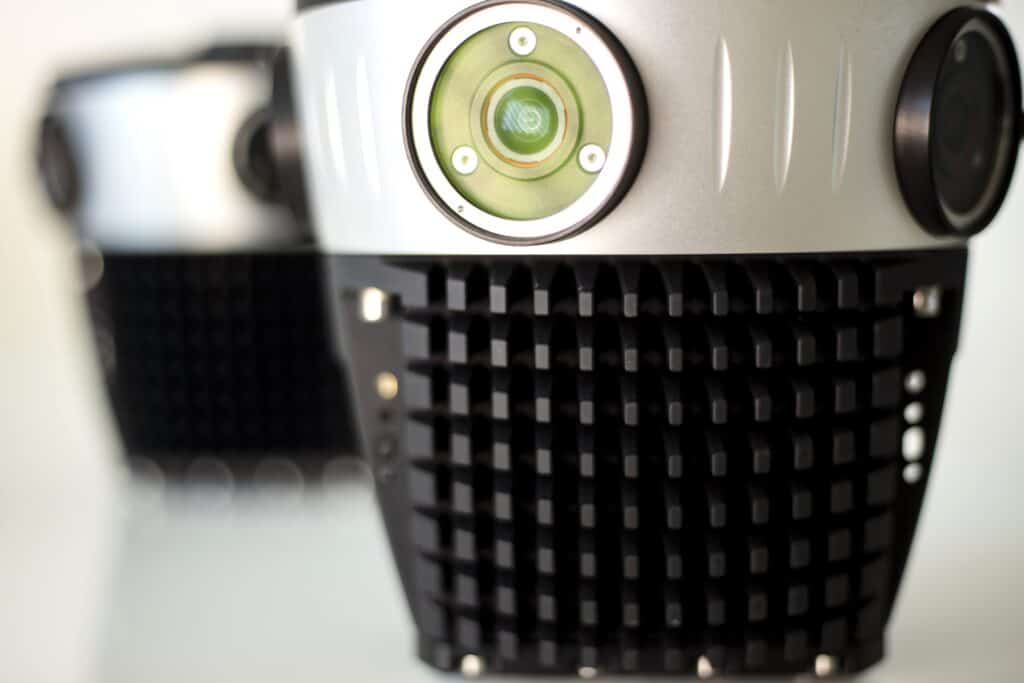

The shift from static to dynamic geospatial mapping
Traditional cartographic methods have inherent limitations in capturing, representing, and analyzing geospatial data. On the other hand, modern mobile mapping solutions leverage advanced remote sensing technologies like LiDAR to create highly detailed three-dimensional point clouds.
Mosaic’s 360-degree HD imaging produces data for extremely rich point clouds of large–scale environments with or without other sensors like GNSS for even more precision and geo-reference.
Traditional mapping vs. modern techniques
Considering the scale of reality capture projects -which often involve hundreds of kilometers of road, asset, or landscape surveying- mobile mapping has become a vital technology to large GIS projects. Its greatest benefit is reducing the time necessary for the data capture.
An adequate level of detail is necessary to get an accurate 3D digital twin for more informed decision-making about assets or even entire landscapes so any deficiency and potential risk is captured and can be analyzed.
Mosaic mobile mapping solutions
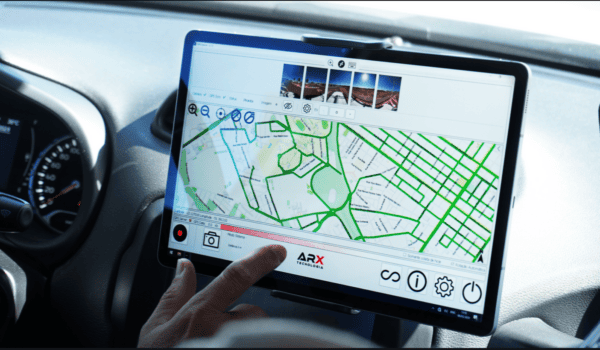
Mosaic’s mobile mapping cameras for HD surveying, GIS, and infrastructure inspection (Mosaic X) are designed to offer the highest resolution on the market. They are robust to withstand challenging weather conditions and are equipped with large internal storage for all-day operations at high speeds.
These features, along with great stitching technology and reliable data for machine learning, are drivers of success in Mosaic customers’ diverse surveying projects like:
- Field, a Nordic powerhouse benefiting from easier road network management
- U.S.-based Midwest Energy & Communications, with their innovative approach to utility mapping for greater network coverage
- Dymaxion, in Colombia, which offers various products to their end users by capitalizing on their Mosaic 51 cameras for electrical grid and road inspection
High-resolution 360 imaging and Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Understanding BIM
BIM is a collaborative process that allows architects, engineers, developers, contractors, manufacturers, and other construction professionals to plan, design, and monitor a structure or building within one 3D model during any phase of its life cycle. Naturally, the more reality-capture technologies evolve, the more innovative solutions they bring along.
A Gauzilla timelapse of splats from a Skender Construction site source
Enhancing BIM with high-resolution data
Reality capture is bringing modern BIM:
- Enhanced Visualization: High–definition 3D imaging and modeling of the surrounding environment allows construction professionals to visualize the construction in a very precise context and increase engagement across all project stakeholders.
- Increased Accuracy and Efficiency: Advanced surveying technologies produce precise, geo-referenced, and scaled 3D models while decreasing the amount of manual effort. Thus, reducing the trips to the construction site and minimizing the risk of errors and rework.
- Enhanced decision making: Consistent and reliable high–definition reality capture data allow for data-driven decisions and easier machine learning integration.
Mosaic’s mobile mapping cameras contribute to BIM, as they allow fast and centimeter-accurate 3D modeling. Highlights include:
- Highest resolution in the market (12K, 13K, and 20K)
- Easy and single-manned operation with minimal training
- 360º Mobile Mapping Backpack solutions for hard-to-reach environments
- Image data for photorealistic environments (including color and texture)
- Centimeter-level accuracy (with LiDAR integration)
- Robust industrial frame & connectors to withstand challenging weather and road conditions
- Non–vendor locked data
Moreover, data from Mosaic 360° cameras can be combined with drone imagery to scan large objects with detailed scenes and textures. See Mosaic’s 3D model of St. Barbara Cathedral.
The future of reality capture is on its way
AI and machine learning (ML) in reality capture
AI and machine learning (ML) are not just industry jargon but practical applications that streamline workflows and enhance efficiency beyond GIS and mobile mapping applications.
With the use of reliable data, AI is assisting industries in uncovering actionable data insights, consolidating their data assets, and optimizing their workflows, like in the case of:
- Predictive analytics: By applying ML and data analytics techniques, AI algorithms can analyze large-scale reality capture datasets to identify patterns, trends, or anomalies as base data for predictive maintenance and risk assessment.
- Automated Data Processing: AI can facilitate recognizing and understanding objects within captured data. By applying deep learning techniques, AI algorithms can automatically identify and classify objects, such as buildings, vegetation, or road infrastructure. This enables more efficient extraction of information and a better understanding of the captured reality.
Integration with IoT
In today’s smart devices ecosystem, the rise of reality capture integration with IoT devices means a cohesive solution that enhances asset operations with one of the most valuable features – real-time. Aligning up-to-date 360-degree photo documentation with precise models from laser scans can bring unprecedented visibility into project status updates.
Reality capture for smart city infrastructures
Smart urban transformation, driven by the integration of continuously developing mobile mapping technologies and data-driven solutions, offers a growing number of benefits for cities and their citizens. From smarter traffic management and infrastructure adjustments to construction planning, accurate reality capture produces higher ROI by keeping projects in-budget and delivered on time.
Emerging technologies
Drone mapping: Aerial imagery in reality capture is rapidly evolving, offering new possibilities for efficient data collection, particularly in hard-to-reach or hazardous areas. Drone technology is enabling the creation of high-resolution 3D models and topographic surveys. It is also an excellent way to extend and complement terrestrial surveying methods.
Modern reality capture is emerging in the world of Augmented and Virtual Reality, with applications far beyond the world of gaming. Advanced VR systems allow for immersive inspection of very complex environments and direct interactions with the objects in the virtual scene. This brings cost-saving benefits, such as reducing field trips for decision-makers, enhancing all possible workflows, and increasing safety for inspection personnel.
Using a VR app to remotely annotate observations (source)
Conclusion
Reality capture technology has emerged as a transformative force in the geospatial industry, fundamentally transforming the way professionals approach GIS, mapping, and BIM projects.
By integrating high-definition imaging, LiDAR scanning, and advanced surveying solutions, organizations can now create unprecedented digital representations of our physical world with remarkable precision.
Mosaic’s cutting-edge 360º mobile mapping cameras stand at the forefront of this revolution, offering industry-leading resolution up to 12.3K, 13.5K, and 20K and robust GNSS and LiDAR integration. Combined with their weather-resistant design and extensive storage capacity, these capabilities enable professionals to capture vast amounts of georeferenced data in a single operation and at highway speeds.
Reality capture is becoming increasingly unified, autonomous, and intelligent through AI-powered analytics, IoT integration, and automated processing. It is breaking down traditional data barriers while enabling seamless virtual site exploration. Organizations that embrace these innovative approaches, including emerging technologies like drone mapping and virtual reality, will be better positioned to meet the growing demands of smart city development, infrastructure management, and environmental conservation.
The revolution in reality capture is not just about collecting data, but transforming how we understand, interact with, and shape our world.