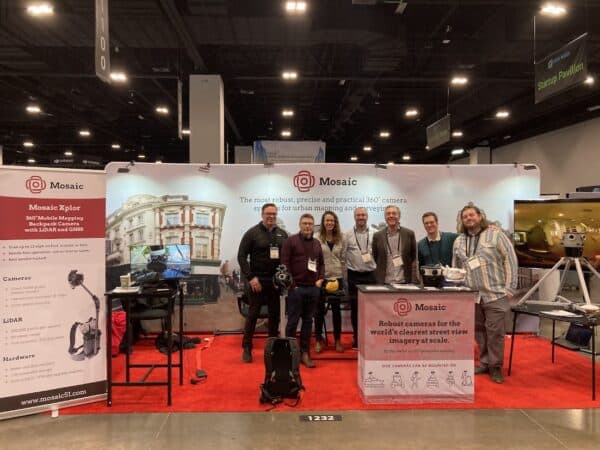
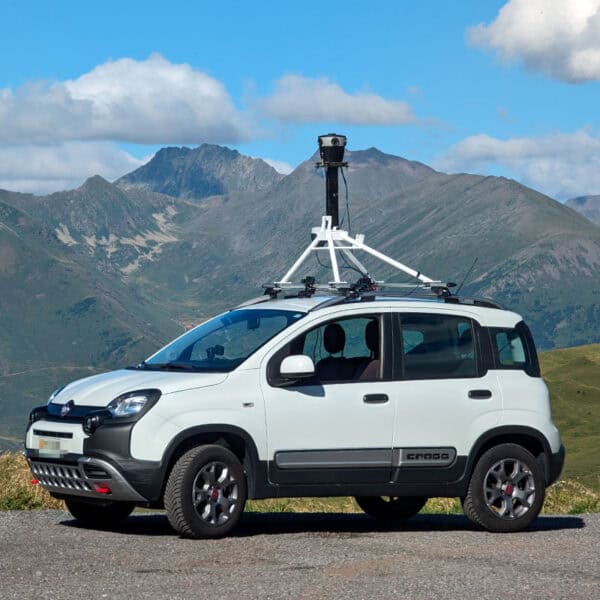
Why the idea on street view imagery collection with mobile mapping is changing course and moving towards reality capture ground truth collected with 360º cameras
In the ever-evolving world of mobile mapping systems, the collection and utilization of street view data have emerged as vital components. Mobile mapping systems are transforming the way we perceive and interact with our surroundings, providing valuable insights for a wide range of applications. Among these, street view data stands out as a crucial element, offering a comprehensive and immersive understanding of the environment. In this article, we will explore the significance of street view data / reality capture collected by 360º mobile mapping cameras, shedding light on its various applications and future possibilities.
Skip to the bottom to learn the ‘Top 5 Benefits of High quality Street View Imagery’ as told to us by our customers.
Or check out another other article about reality capture in the AEC industry –>
Evolution of Mobile Mapping Systems
Before the advent of mobile mapping systems, reality capture data collection was predominantly carried out through time-consuming ground-based measurements or costly aerial surveys. These methods had limitations in terms of accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility. However, with the introduction of mobile mapping systems, these limitations were overcome. These systems revolutionized the way data is collected by combining advanced technology and mobile platforms, providing real-time, high-resolution street view data, with a reduction in the time, costs and man-power necessary.
Understanding Street View Data
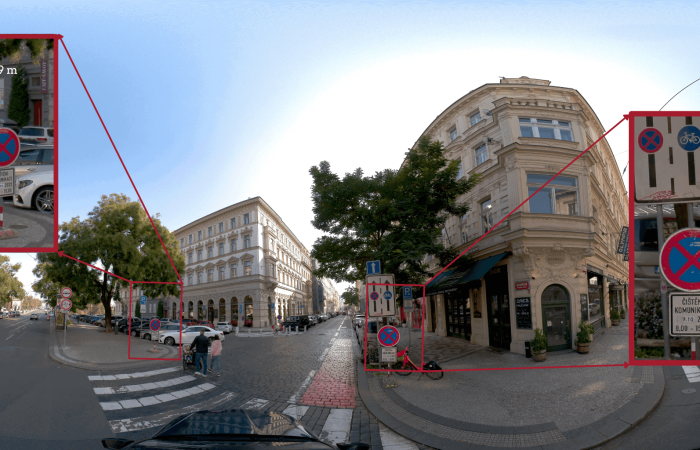
Street view data encompasses a rich collection of information, comprising imagery, geospatial data, and (sometimes) point cloud data. The imagery component captures the visual representation of the environment, providing a detailed snapshot of streets, buildings, and landmarks. Geospatial information can be layered with location-specific data, such as coordinates, addresses, and other geographic attributes. Point cloud data, obtained either through laser scanners (LiDAR) or through 360º mobile mapping cameras paired with RTK GPS data, enables the creation of precise 3D models and enhances the overall accuracy of the mapping system.
Definition and Components of Street View Data
Imagery
Imagery forms the reality capture visual component of street view data. It consists of high-resolution photographs captured by 360º mobile mapping cameras. These cameras capture highly realistic images from multiple viewpoints, allowing for a complete and immersive visualization of the streets, buildings, landmarks, and other features in the environment. The imagery provides a realistic and detailed representation, enabling analysts, researchers, and users to observe and analyze the surroundings with precision.
Geospatial Information
Geospatial information refers to the location-specific data associated with street view data. It includes coordinates, addresses, and other geographic attributes that enable accurate geolocation and spatial referencing of the captured imagery. Geospatial information plays a vital role in integrating street view data with other geospatial datasets, facilitating advanced analysis and visualization. Users can achieve a comprehensive understanding of the environment by combining street view data with other geospatial information, such as road networks, land use data, or topographic features.
Point Cloud Data
Point cloud data is a critical component derived from 360º mobile mapping cameras. It represents a three-dimensional collection of points in space, capturing the geometry and spatial characteristics of the environment. Point cloud data is obtained through laser scanning or LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology. This technology emits laser beams and measures the time it takes for the beam to return after hitting an object. This data, combined with the imagery, allows for the creation of precise 3D models of the environment. Point cloud data enhances the accuracy and spatial understanding of mobile mapping systems, enabling detailed analysis, measurements, and simulations.
By combining imagery, geospatial information, and point cloud data, street view data provides a comprehensive and multidimensional representation of the environment. It allows for detailed visual analysis, precise geolocation, and accurate 3D modeling, making it a fundamental component in the field of mobile mapping systems. The integration of these components enables a range of applications, including urban planning, transportation systems, virtual tours, and environmental analysis. As technology advances, street view data continues to evolve, providing increasingly accurate and detailed insights into our surroundings.
Importance of Street View Data in Mobile Mapping Systems
Street view data plays a pivotal role in mobile mapping systems, enabling accurate and precise mapping of our surroundings. The high-resolution imagery captured by 360º mobile mapping cameras allows for detailed visual analysis and identification of objects and features. Multiple viewpoints obtained by these cameras provide a comprehensive understanding of the environment, minimizing occlusions and ensuring complete coverage. Moreover, the integration of geospatial information enables precise geolocation and spatial referencing of the collected data.
Accuracy and Precision in Mobile Mapping Systems
Accurate and precise data collection is crucial in mobile mapping systems to ensure reliable and high-quality results. The advancements in 360º mobile mapping cameras have significantly contributed to improving the accuracy and precision of data capture. Let’s explore the role of these cameras and the utilization of geospatial information in achieving accurate and precise mapping:
Role of 360º Mobile Mapping Cameras in Capturing Accurate Data
High-resolution Imagery
360º mobile mapping cameras capture high-resolution imagery, also known as ‘reality capture’, providing detailed visual information about the environment. The high resolution allows for the identification and analysis of small objects, textures, and intricate details. This level of detail enhances the accuracy of mapping systems by minimizing errors and providing a more realistic representation.
Multiple Viewpoints
One of the significant advantages of 360º mobile mapping cameras is their ability to capture images from multiple viewpoints. These cameras are equipped with a combination of wide-angle lenses allowing them to capture the environment from different angles simultaneously. By capturing multiple viewpoints, the cameras can reduce occlusions caused by obstructions and capture a clear understanding. This comprehensive coverage ensures that no significant details are missed, resulting in more accurate and reliable data.
This is also important for creating context for the viewer. A single angle shot may not provide the context for the user that a 360º view can.
Utilizing Geospatial Information for Precise Mapping
Geospatial information plays a crucial role in achieving precise mapping in mobile mapping systems. By integrating geospatial data with street view data, precise geolocation and spatial referencing can be achieved. Here’s how geospatial information contributes to precise mapping:
Accurate Geolocation
Geospatial information, such as coordinates and addresses, provides accurate geolocation for the captured imagery and point cloud data. By precisely locating each piece of data within the geographic space, the mobile mapping system can accurately map the features onto the real-world coordinates. This accurate geolocation enables precise mapping and alignment with other geospatial datasets, ensuring consistency and accuracy in the final mapping results.
Spatial Referencing
Geospatial information also facilitates spatial referencing of the captured data. By associating each data point with its corresponding geospatial attributes, such as road networks, topographic features, or land use data, the mobile mapping system can create a spatial context for the captured imagery and point cloud data. This spatial referencing allows for advanced analysis, such as overlaying the street view data with other datasets or conducting spatial queries and analysis based on specific geographic attributes.
By leveraging the capabilities of 360º mobile mapping cameras and utilizing geospatial information, mobile mapping systems can achieve a high level of accuracy and precision in data capture and mapping. The combination of high-resolution imagery and multiple viewpoints ensures a comprehensive and detailed representation of the environment. Integrating geospatial information enables accurate geolocation and precise spatial referencing, enhancing the reliability and usability of the mapping data. With these advancements, mobile mapping systems are becoming increasingly valuable in various domains, including urban planning, transportation, and environmental analysis.
Applications of ‘Reality Capture’ Street View Data
The applications of street view data in mobile mapping systems are vast and diverse. In urban planning and infrastructure development, street view data helps professionals visualize and analyze existing structures, plan new developments, and assess the impact of proposed changes. Transportation and navigation systems rely on street view data to provide accurate and up-to-date information to users, enabling efficient routing and navigation. Street view data is also extensively used in creating virtual tours and promoting tourism, allowing people to explore places remotely. Furthermore, street view data contributes to environmental mapping and analysis, aiding in the monitoring of vegetation, land use, and ecological changes.
Check out this full article on the applications and use cases for 360 street view imagery.
Enhancing Data Analysis and Visualization
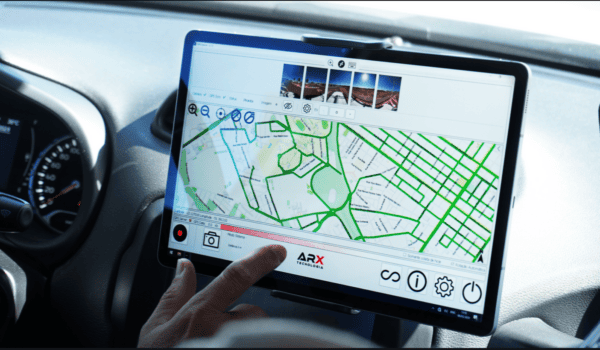
The integration of street view data with other datasets amplifies its value in mobile mapping systems. By combining street view data with aerial imagery, satellite data, or IoT sensor data, a comprehensive understanding of the environment can be achieved. This integration enables advanced data analysis techniques and facilitates 3D modeling and simulation, creating realistic virtual environments for various applications. Street view data serves as a rich source of information, allowing analysts and researchers to extract actionable insights for decision-making processes.
Here is one such example. Check out this street-view data set from the Mosaic X camera combined with aerial data from a drone, creating a complete 360º view of the town of Terezin, Czech Republic (just north of Prague where Mosaic is based). (full model)
5 Reasons why the imaged-based mobile mapping field is growing
- Monopolizing on existing technology or workflows
Many surveying companies already have vehicles collecting data with other sensors, or just driving to locations for surveys. Aggregating a 360º mobile mapping camera to the surveying vehicle already in-use requires much less effort then starting from scratch and eliminates the need to acquire additional vehicles. - Slow movement from key players
The dominant players (mainly Google) do not update fast enough. While many agencies and organizations have relied on Google Street View to fulfill their street level imagery needs, Google is not a reliable source for up-to-date information. Depending on the country and the region, these maps may go 3, 5, even 9 years without updates. A lot can change in that time, meaning the data being displayed can be irrelevant.
Google Street View coverage as of 2023. If you notice that there seem to be some gaps, you’re not wrong.
- Lack of coverage
Not only is it not up to date, but Google Street View also just doesn’t cover enough grounds. (see the image above). Many rural areas and developing countries are not mapped nearly as much as countries that tend to find themselves in the OECD. - Humans perceive in images
Sometimes images are better than even highly-dense and rich point clouds and are the source of information that people actually need. While point clouds have been all the rage for the last decade or so, many times a point cloud is not comprehensible to the average end user of the data. Point clouds may be accurate, but they are not as easy on the eyes to untrained observers. If a picture is worth 1,000 words, then what is a 360º image worth? (please tell us – we aren’t sure how to calculate this!) - LiDAR is overkill.
Not only might it not be easy to understand, but using LiDAR is sometimes like killing a fly with a sledgehammer. It collects a massive amount of data that requires considerably processing. And this collection and processing must be done by a highly trained individual during data capture. Laser scans and point clouds are not easily viewed or navigated without special hardware and software. Additionally, laser scan files are large, making them difficult to process and share.
Here’s why mobile mapping cameras may be the better option
5 Benefits of higher quality reality capture at scale
In speaking with our customers, this is what we hear about how higher quality imagery, captured at scale with Mosaic cameras, is improving their lives, workflows, and outputs.
- Reduce (or eliminate) site visits / Minimize time in field
Capture the data once on the road and then surveyors or end users of the data don’t need to return to gain a very good understanding of the situation. Users can look up what are the most current conditions and have a clear understanding.
“We’ve scaled a long way without increasing our site resources because 70% of work is done by the office resources we have (compared to traditional surveying methods)”
– Dan Davis (Learn more about how Catsurveys in the UK capitalized on their Mosaic 51 cameras) - Make data collection safer
Especially on highways or train lines. One of the biggest dangers for surveyors is traffic. Surveyors often need to collect data along busy roads, requiring them to step out of their vehicles along highways with traffic passing at high speeds. By remaining inside the vehicle and collecting the necessary data while moving with the flow of traffic, companies can confidently send their employees to the field without having to be concerned for their safety. - Reduce costs of data collection
With a simple and easy to use mobile mapping camera, the time for onboarding, training and daily day captures is significantly reduced. The Mosaic 51 and Mosaic X cameras were designed to be very easy to learn to operate. Rather than having to utilize trained surveyors or mobile mapping experts, companies can use other employees or hire drivers to simply drive and collect data. - Speed up data collection time
Driving at normal city or highway speeds with a high-resolution 360º camera significantly speeds up the collection workflow compared to walking and taking notes along the way or using total stations (instruments that must be placed in one location to collect data).
“I could do what it used to take two of us to do, right? And that was a project. we could boil it down to just one person. I think that that alone speaks volumes. I would estimate our workflow speed increase, about double to quadruple.”
– Dylan Faraone (Check out more about Site Tour 360’s use of the Mosaic 51 camera post Hurricane Ian) - Make more data accessible to more people
Images are much more understandable to humans compared to other forms of visualization (i.e. point clouds). Using photographs means more people can access and gain insight from the data collected with cameras.
This means that more members of the company, more government officials and key decision makers can benefit from the data.
Additionally, Mosaic camera data comes non-vendor locked, so users can determine the workflow and processing that best suits their needs.
“One of our previous cameras with a built-in software entails relatively high software update and license renewal costs, especially because of the different currencies. So, it is great that with Mosaic, we can make our own solution for post-processing without having to renew a software contract year after year.”
– Gustavo Guevara from Dymaxion (Learn more about Dymaxion’s use of the Mosaic 51 for utility inspection and road surveying)
Future Trends in Mobile Mapping Systems
We see that the field of mobile mapping systems is poised for exciting advancements and we’re very excited to be along for the ride. Technological innovations in camera technology will continue to enhance the capabilities of 360º mobile mapping cameras. This will enable higher resolution imagery, improved depth perception, and extended coverage. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms will empower systems to automatically extract features, recognize objects, and enhance data processing. Real-time data collection and analysis will become more prevalent, allowing for immediate updates and dynamic decision-making in various domains.
Street view data collected by 360º mobile mapping cameras is indispensable in the field of mobile mapping systems. Its significance lies in its ability to provide accurate, detailed, and immersive information about our surroundings. From urban planning to navigation systems to environmental analysis, the applications of street view data are extensive and diverse. As technology continues to advance, the future of mobile mapping systems holds exciting prospects, promising further enhancements in data collection, analysis, and visualization.
If you’re looking to speed up data collection, increase safety for your employees, and make data more accessible and understandable to your end customers, then contact our team today.