From collision avoidance to autonomous driving
Road to safety and convenience
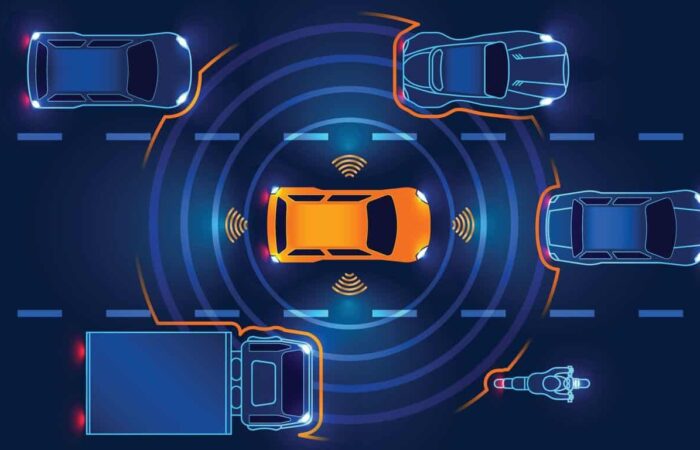
It is, unfortunately, still human error which remains the most significant factor in car accidents. In the US, for example, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), 94% of motor vehicle crashes involve driver error. To ensure that critical situations end in the best possible way and to make driving more convenient, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS for short) are now available in an increasing number of cars and trucks. How do these automated systems make driving safer, easier, and more comfortable while avoiding or reducing the negative consequences of choices made by the driver? What is the role of HD mapping in ADAS systems anatomy, and how does it bring us closer to autonomous driving?
ADAS anatomy: from sensors to software
Sensors
To assist the primary decision makers behind the wheel and to make sure that adequate safety measures are taken, the forces of multiple sensors are joined, which involve:
Camera sensors feed directly into the ADAS computer, which identifies different objects such as pedestrians, street signs, lane markings, and other vehicles.
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) allows ADAS to draw data from multiple satellite constellations to more accurately determine a vehicle’s location and orientation.
Radar systems use radio waves to detect surrounding objects, helping power ADAS features like blind spot monitoring, pedestrian detection, adaptive cruise control, and parking assist.
Sonar sensors employ sound waves instead of radio waves. Using air as the medium, sonar performs optimally at lower speeds or when the car is still.
Lidar systems use light waves to detect surrounding objects in the form of lasers with extreme precision.
Software
With drivers expecting their rides to be as smart as their phones, car companies rely almost as much on software as they do on the actual vehicle. ADAS systems are becoming more effective and are seeing an increased adoption with the use of digitization technologies such as cloud, mobility, deep learning and artificial intelligence.
Processors
Used for everything from building a real-time 3D spatial model of a car’s surroundings to calculating proximity and threat levels based on the environment.
Actuators
With all the processed data from the sensors and the ADAS system, the resulting decision can be put into practice by actuators supporting everything, right from electric power steering to autonomous acceleration and breaking.
Mapping systems
These systems utilize 3D and HD maps and real-time data to enhance drivers’ awareness and decision-making capabilities beyond what traditional sensors alone could provide. By incorporating detailed information about road geometry, traffic signs, and other static elements, map-based ADAS enables more precise navigation, predictive driving, and improved safety features.
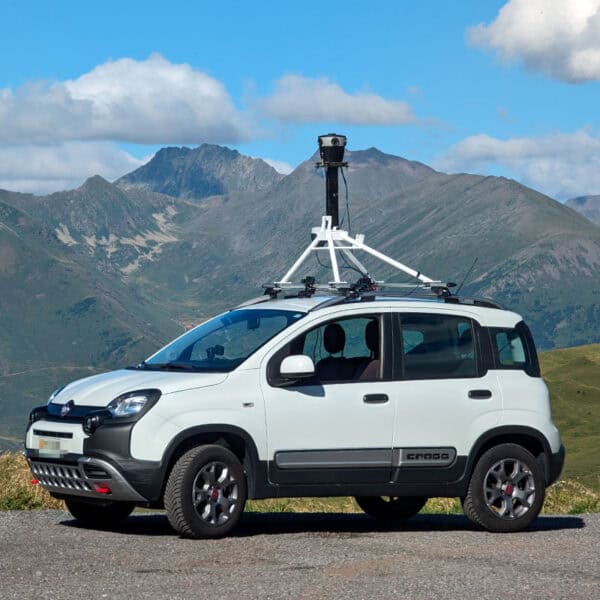
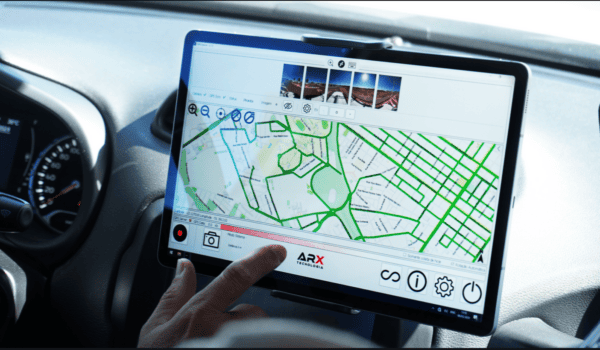
Modern mapping systems utilize high-definition imagery and real-time data to create comprehensive 3D and HD maps that enhance driver awareness and decision-making capabilities. Advanced mobile mapping technologies, capable of capturing 360-degree street views, are essential for developing these detailed maps. By continuously collecting and processing visual information, these systems keep digital maps current and reliable, ensuring that advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) remain effective as road networks evolve.
Map-Based ADAS: from collision avoidance to autonomous driving
While the increasing affordability and popularity of ADAS have brought us closer to the reality of self-driving vehicles, it is not ADAS technology alone that fully enables autonomous cars. The key challenge remains to localize the vehicle in real-time and with that level of precision as human sight would do. Another key challenge is naturally to interpret the information with similar capabilities of human drivers but ideally without their errors.
The importance of HD mapping: because sensors are not eyes
Real-time computing and onboard sensors alone can’t handle the complexity of roads and traffic. In such a way, HD maps become critical for the guidance of autonomous cars. They improve sensor perception in extreme weather conditions or at a very close range and are able to recognize objects and events that might otherwise go unnoticed by intelligent onboard sensors. HD maps for autonomous driving provide cm-level accuracy, detailing pedestrian crossings, traffic signals, and barriers. Markus Grünke, cartographer and project manager at 3D Mapping Solutions, compares an HD map to an additional high–performance sensor. While LiDAR sensors on the roof of vehicles can record one million points per second to create millimeter precise 3D maps, HD cameras supply the 3D model with color and information about the exact time and place.
HD mapping technology is crucial in autonomous vehicles by providing centimeter-level precision that complements traditional sensor data. High-resolution 360-degree street-level imagery is essential for building these maps, offering a detailed view of lane markings, traffic signs, and other crucial elements. Such technology ensures that autonomous systems have the reliable and updated visual information necessary for precise localization and safe navigation, even in challenging conditions.
Benefiting from this, map-based ADAS leverages detailed digital maps and real-time positioning to provide advanced features such as predictive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and proactive safety alerts. These systems use map data to anticipate road conditions, curves, speed limits, and other factors beyond the range of traditional sensors, allowing for more informed and anticipatory driving assistance.
Ultimate benefits of map-based ADAS and AV mapping
When everything that is pre-mapped is combined with real-time sensor inputs, the outcome is a very comprehensive and detailed understanding of the vehicle’s environment.
Map-based ADAS technologies combine real-time sensor inputs with detailed HD maps to deliver a comprehensive understanding of the driving environment. High-resolution mapping systems, capable of documenting road networks and infrastructure with precision, are vital to this process. By integrating high-quality imagery and dynamic map updates, these systems enhance adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and other advanced features, contributing to safer and more efficient vehicle navigation.
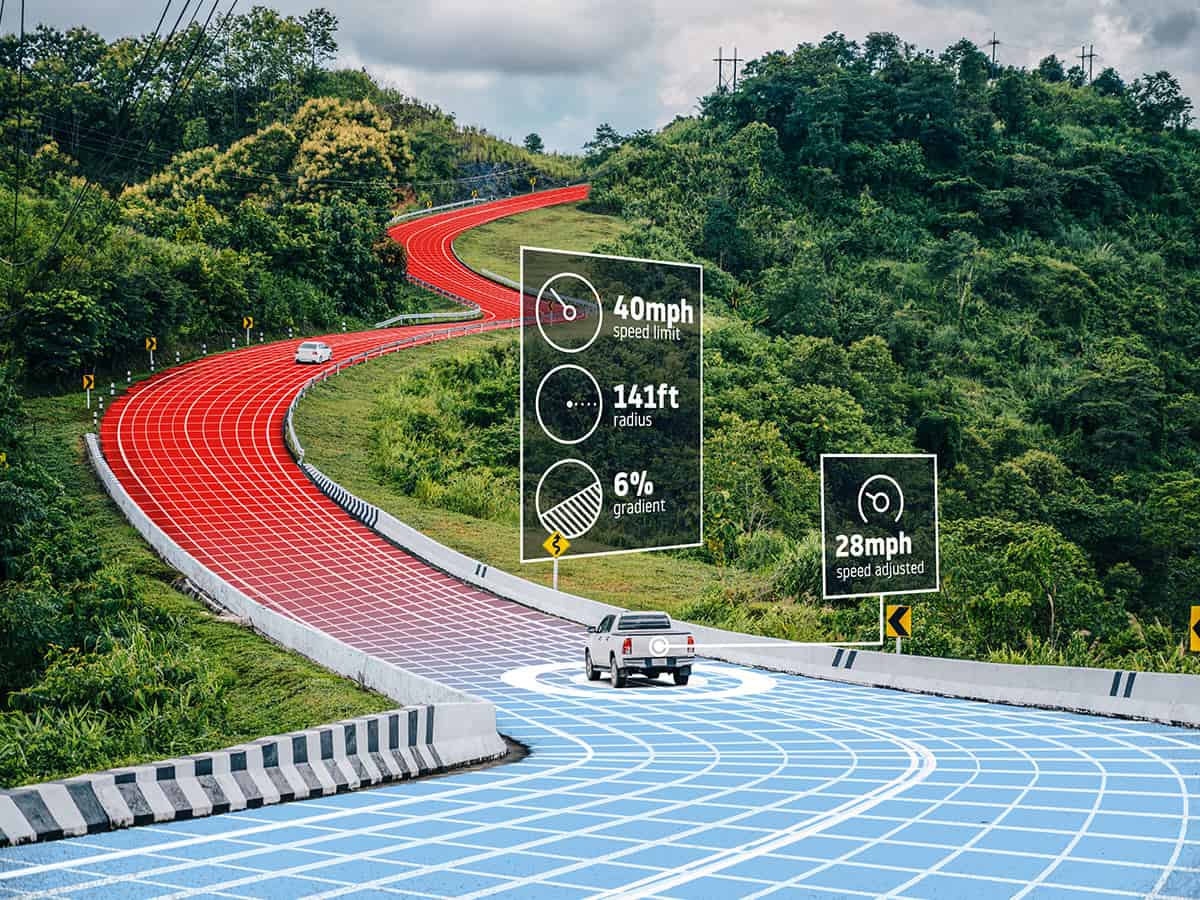

Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
ACC uses radar or camera sensors to detect vehicles ahead and adjust the speed accordingly and map data to adjust vehicle speed based on upcoming curves and speed limits.
Lane Keeping Assist (LKA)
LKW (lane-keeping warning) systems alert the driver when the vehicle unintentionally drifts out of its lane, while LKA takes it a step further by providing gentle steering input to keep the vehicle centered in its lane. It uses lane-level accuracy from HD maps to guide steering.
Real-time navigation and traffic updates
Real-time data integration with HD maps allows the ADAS to maintain a very up-to-date picture of its environment and traffic conditions, such as road work, accidents, and other emergencies. This feature also allows ADAS and potentially AV to plan the most efficient route and avoid delays caused by traffic jams or other obstacles.
Advanced mobile mapping systems equipped with high-resolution cameras are essential for real-time navigation and traffic updates. These systems capture dynamic changes on the road, ensuring that ADAS features like traffic rerouting and hazard detection are based on the most current and accurate data available.
Smarter maps, smarter drivers
While most of the world’s road population is still somewhere between level 0 and 2 in driving automation (0 automation – 1 driver assistance – 2 partial driving automation), undisputable benefits of map-based ADAS technologies can be observed, such as:
Enhanced situational awareness and decision-making
By providing very detailed and comprehensive information about the car’s environment, driving assistance systems can change the way we drive. This naturally allows the ride to become smoother, more predictable and without aggressive elements.
Reduced driver fatigue and stress
When driving, drivers are often overloaded with too much information to process. As a result, stress or fatigue levels naturally rise. Map–based and other ADAS systems have been continuously developing to help drivers focus on the primary driving tasks. Some of the ADAS systems are even designed to monitor driver fatigue and warn them ahead.
Detailed HD maps, powered by high-definition imagery and real-time data, enhance situational awareness and decision-making for ADAS and autonomous systems. By providing a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s environment, these mapping technologies allow for predictive driving and improved safety features. Integrating such technology helps create smoother, more efficient rides, reduce driver fatigue, and enable smarter, more informed driving assistance.
Increased safety and accident prevention
Map-based ADAS systems significantly enhance road safety and accident prevention by providing vehicles with advanced knowledge of upcoming road conditions, hazards, and traffic patterns.
HD maps to improve accuracy and reliability in AV performance
By combining real-time sensor data with pre-mapped information, AVs can make more informed decisions, react more effectively to their surroundings, and operate more safely, even in challenging conditions.
The development of HD maps relies heavily on high-definition imagery captured by advanced mapping technologies. These systems provide the real-time visual information needed to create accurate maps that support autonomous vehicle decision-making, even in complex or changing environments.
Integrating map-based ADAS systems on the road to driving autonomy
Although we are still years of research and development away from fully automated driving, the market leaders in the autonomous vehicle industry have been continuously pushing the boundaries of what’s possible:
Tesla’s Autopilot
A pioneer in consumer-facing autonomous technology, Tesla has developed a sophisticated Level 2 automation system. This AI-driven platform builds upon Tesla’s core ADAS, offering features like adaptive cruise control, automatic parking, and highway navigation. While Autopilot relies primarily on visual perception using the eight cameras around the vehicle plus additional input from a forward-facing radar unit and ultrasonic sensors, Tesla confirmed in a one-word tweet it is likely to utilize crowdsourced high-precision maps to help the Autopilot system better navigate with precision and avoid obstacles like potholes.
Source: autopilotreview.com
Motional
This 2020 joint venture between Hyundai and Aptiv is at the forefront of Level 4 autonomy for ride-hailing and delivery services. With over 125,000 autonomous rides completed in Las Vegas via Lyft, Motional expanded to Uber in late 2022. The company has been aiming to launch fully driverless services in Las Vegas, with plans to expand to other major U.S. cities.
Mapping is one of the first tasks our teams undertake when we enter a new city. We create high-definition maps of the driving environment that feature centimeter-level precision and help the vehicle understand where it is, what’s around it, and where it should move next.
Cruise
Global Motor’s autonomous driving subsidiary has made significant strides since its 2013 founding. In 2021, Cruise achieved a major milestone by offering the first fully driverless taxi rides in a major U.S. city. By early 2023, its autonomous fleet had impressively logged over one million driverless miles.
Cruise’s move to develop HD maps is one of the few major efforts by an automaker to grow the technology in-house. Most other automakers rely on partnerships with suppliers and tech companies to get their digital maps.
Waymo Driver
Alphabet’s self-driving unit has been making waves in the AV industry. As of 2023, Waymo is testing its latest autonomous EV, the Firefly, in Austin. The company’s Waymo One ride-hailing service is already operational in Phoenix and San Francisco. To create a map for a new location, Waymo uses a custom lidar to create a 3D map of the new environment to provide meaningful context for the Waymo Driver.
Miles to go before ADAS and AVs can fully rely on HD maps
As discussed earlier, HD mapping plays a crucial role in the development of ADAS systems and AVs towards accurate perception of the environment, critical decision making and overall road safety. Precise and up-to-date HD maps provide essential information for safe and efficient navigation. Logically, creating and maintaining HD maps for ADAS and AVs comes with significant challenges.
Vast amount of data
HD cameras and GPS/GNSS collect information about road networks, infrastructure, and the surrounding environment but produce immense data. The fastest and most reliable way to resolve that issue is through comprehensive, cloud-based navigation platforms, which integrate map collection, aggregation, and maintenance features. Based on the cloud, these features provide enough storage and high-performance computing power capabilities to support the demanding autonomous driving infrastructures.
HD map accuracy and precision
HD maps for AVs require an unprecedented level of accuracy and precision. Even small discrepancies in map data can lead to dangerous situations. Achieving centimeter-level accuracy in HD maps is a significant technical challenge, particularly in environments that are constantly changing. High-resolution mobile mapping technologies are designed to meet these demands, capturing precise imagery of road networks, traffic patterns, and infrastructure. This data is then integrated into HD maps to maintain the accuracy required for safe and effective autonomous vehicle navigation.
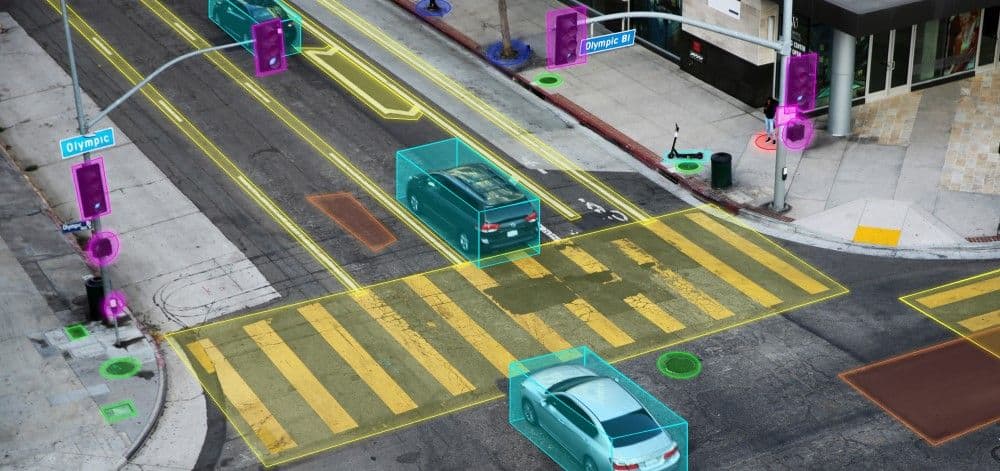
Real-time updates and map maintenance
The driving environment is an object of continuous change. Road construction or sudden road damage, new traffic signs, and other modifications require up-to-date information in a real-time HD map, which is a monumental task. Detecting, validating, and incorporating these updates into the map system efficiently requires high-speed bandwidth and support for high vehicle density. The existing V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) networking and connectivity capabilities don’t provide these. Transmission allocation and cache allocation improvements are being made to reduce delays in HD map delivery, but latency remains an issue.
To maintain accurate and up-to-date HD maps, real-time data collection and processing are essential. Mobile mapping systems equipped with advanced imaging technologies are key in gathering the necessary information to document and update road conditions, traffic signals, and other infrastructure changes. By rapidly integrating this new data, such technologies enable ADAS and autonomous vehicles to operate with the most current information, adapting to dynamic environments efficiently.
Scalability and Coverage
Creating HD maps for small, controlled environments is one thing, but scaling this process to cover entire cities, countries, or even globally presents a significant challenge. The scale of data collection, processing, and storage required for worldwide coverage is enormous.
Scaling HD maps for widespread deployment requires advanced technologies capable of capturing high-resolution imagery over extensive road networks. These mapping systems provide the foundational data needed to maintain the accuracy and consistency of maps at a large scale, supporting the growth of ADAS and AV technologies globally.
Standardization and Interoperability
Individual OEMs, as well as navigation technology and HD mapping companies such as TomTom, HERE Maps, or Nvidia, publish their own maps in proprietary formats; however, the real value of HD mapping for autonomous vehicles can only be realized through standardization. A significant step towards map integrity and consistency of HD mapping was the foundation of NDS (Navigation Data Standards) Association.
Innovation to drive it all
With McKinsey stating that autonomous driving could create US$400bn in revenue by 2035, OEMs are racing in R&D to overcome these challenges, refining and fine-tuning their ADAS systems along the way. The goal remains the same: to enhance road safety and improve the way consumers experience mobility. Emerging trends include:
Crowdsourced Mapping – the direction of, among others, Mobileye, Nvidia, or Tesla’s autopilot aims to leverage data from millions of connected vehicles to continuously update 3D and HD maps in real-time and related advancements in V2X communication.
AI and machine learning – to automate map creation and change detection from raw sensor data and identify and fix point cloud misalignments from SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping).
4D Mapping includes time as a fourth dimension to create maps that can adapt dynamically and in real-time to changing road conditions, traffic patterns, and challenging weather conditions.
Semantic labelling – to incorporate contextual understanding into maps, allowing vehicles to interpret the meaning and function of objects in their environment.
The most important aspect that developments in mobile mapping, ADAS, and AVs are expected to inevitably lead to is an increase in not only road safety (a study used as an example by McKinsey shows that the growing adoption ADAS in Europe could reduce the number of accidents by about 15 percent by 2030) but also improve traffic flow, mobility for non–drivers and even environmental benefits through more efficient driving.

Safe, connected, and convenient future of mobility
Moving forward to the future of autonomous driving, map-based ADAS and HD mapping technologies appear to be crucial components to develop an accurate perception of the vehicle’s environment. They also fine-tune the range of information crucial for the driver’s critical decision-making. These advanced systems have been and will continue to enhance safety but also pave the way for more efficient and sustainable driving. As the industry has been striving to tackle the challenges discussed, innovations in HD mapping, AI, machine learning, and crowdsourced mapping are driving progress toward more efficient ADAS systems and higher levels of automation. The evolution of these technologies promises to revolutionize not just how we drive but how we approach driverless city planning and mobility for generations to come.
Enhancing Mobility with HD Mapping and 360° Imagery
As the demand for safer and more efficient driving solutions grows, the role of HD mapping and advanced mobile mapping technologies continues to expand. These systems, combined with real-time data and high-resolution 360° imagery, are critical to improving road safety and paving the way for autonomous vehicles. By providing precise, real-time insights into road conditions and surrounding environments, map-based ADAS systems are creating smarter and more informed driving experiences.
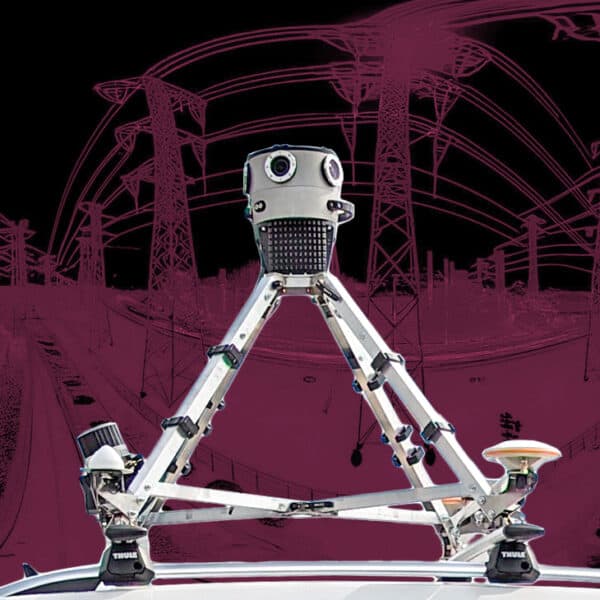
At Mosaic, we produce cutting-edge 360° mobile mapping cameras that support high-definition map creation, allowing for precise data capture in even the most challenging environments. Our technology ensures that ADAS systems and autonomous vehicles are equipped with the detailed visual information they need for accurate navigation and decision-making.
Want to learn more about how Mosaic cameras can enhance your mapping projects? Contact us for more information.